02 Data Lifecycle Management
Age of Digital Transformation
Technological advancements have led to changes in the economy and society. There have been five significant development stages in the last hundrets of years:
- 1785 - 1845: Industrial Revolution
- 1845 - 1900: Age of Steam and Railways
- 1900 - 1950: Age of Electricity, Chemicals and Oil
- 1950 - 1990: Aviation, Petrochemicals, Electronics
- 1990 - 2020: Digital Revolution
- 2020 - 2040: Artificial Intelligence…?
Today we are working in a digital world, where data is the most valuable asset. It is possible to work from anywhere, at any time, with any device. This has led to a massive increase in data generation and storage.
Data
Data is very valuable. It is valued from least to most:
- Raw Data: just data (e.g. logs)
- Subjective Data: interpreted and structured (e.g. opinions, ads)
- General Knowledge: made available to the public (e.g. Wikipedia)
- Contextual Knowledge: made available to selected group (e.g. Manuals)
- Actuality: realtime is more valuable (e.g. News)
- Advantages: data that provides an advantage to the receiving party (e.g. Strategies, Intelligence)
- Intellectual Property: protected knowledge (e.g. Patents)
Important: The value is also influenced by the availability and legality!
Price of Data
The following prices are from an analysis in 2008 from the black market:
| Data Type | Price per Record | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Card | $0.06 - $30 | 32% |
| Bank Account | $10 - $1000 | 19% |
| E-Mail with Password | $0.1 - $100 | 5% |
| E-Mail Address | $0.33 - $100 | 5% |
| Identities | $0.7 - $60 | 4% |
| Spam Sender | $2 - $40 | 3% |
| Phishing Attacks | $2 - $40 | 3% |
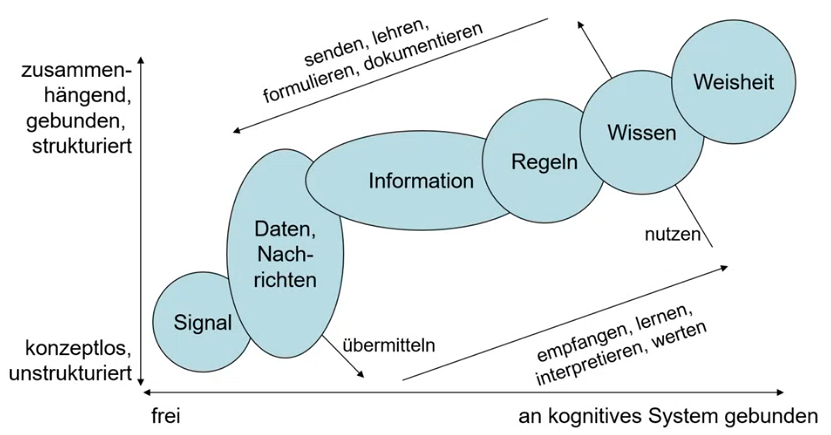
Differentiation of Data
Problems with Data
- Too much or too little data
- Uncertainty about correctness
- Uncertainty about intent
- Uncertainty about completeness
- Uncertainty about timeliness
- Uncertainty about sensitivity
- Uncertainty about context
- Unstructured data
- Legacy data
- Cost of storage and modeling
Data Lifecycle
A data lifecycle consists of many different steps and stages.
- Modeling / Conceptualization: what data do I have and is needed?
- Collection: how do I get the data?
- Integrity: ensure correctness and completeness
- Relevance: rate the relevance of the data
- Classification: classify the data
- Storage: how do I store the data?
- Distribution: how do I distribute the data?
- Conversion: how do I convert the data?
- Categorization: how do I categorize the data?
- Search: make data searchable for later use
- Analysis: analyze the data
- Integration / Correlation: integrate the data with other data
- Backup: how do I backup the data?
- Archiving: how do I archive the data?
- Destruction: how do I delete the data?
- Raw Data: what is raw data?
- Master Data: what is master data?
- Transaction Data: what is transaction data?
- Metadata: what is metadata?
- Deliniation: active or inactive data?
Value Chain
The value chain of data is as follows:
- Collection or Generation (e.g. logs, crm, paper, …)
- Storage (e.g. databases, warehouses, …)
- Validation (e.g. quality, completeness, …)
- Processing / Analysis (e.g. business intelligence, analytics, statistics, …)
- Distribution (e.g. reports, dashboards, …)
Data in ITSM
- Generation of technical data (e.g. logs, monitoring)
- Generation of business data (e.g. crm, erp, documents)
- Management of storage assets (e.g. databases, warehouses)
- Service continuity and availability management
- Knowledge management
Escrow
Escrow is a legal concept where a third party holds something of value until a condition is met. This is often used in software development, where the source code is held by a third party until the software is delivered. This ensures that the software can be maintained and developed further, even if the original developer is not available anymore.