07 LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN is a protocol for low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) that uses LoRa modulation for long-range communication. LoRa is a proprietary modulation technique that uses chirp spread spectrum (CSS) modulation.
Network
The LoRaWAN network consists of three parts:
- Nodes: Devices that send data to the network.
- Gateway: LoRa to Internet (TCP/IP) gateway.
- Network Server: LoRaWAN backend
- Application Server: Application backend
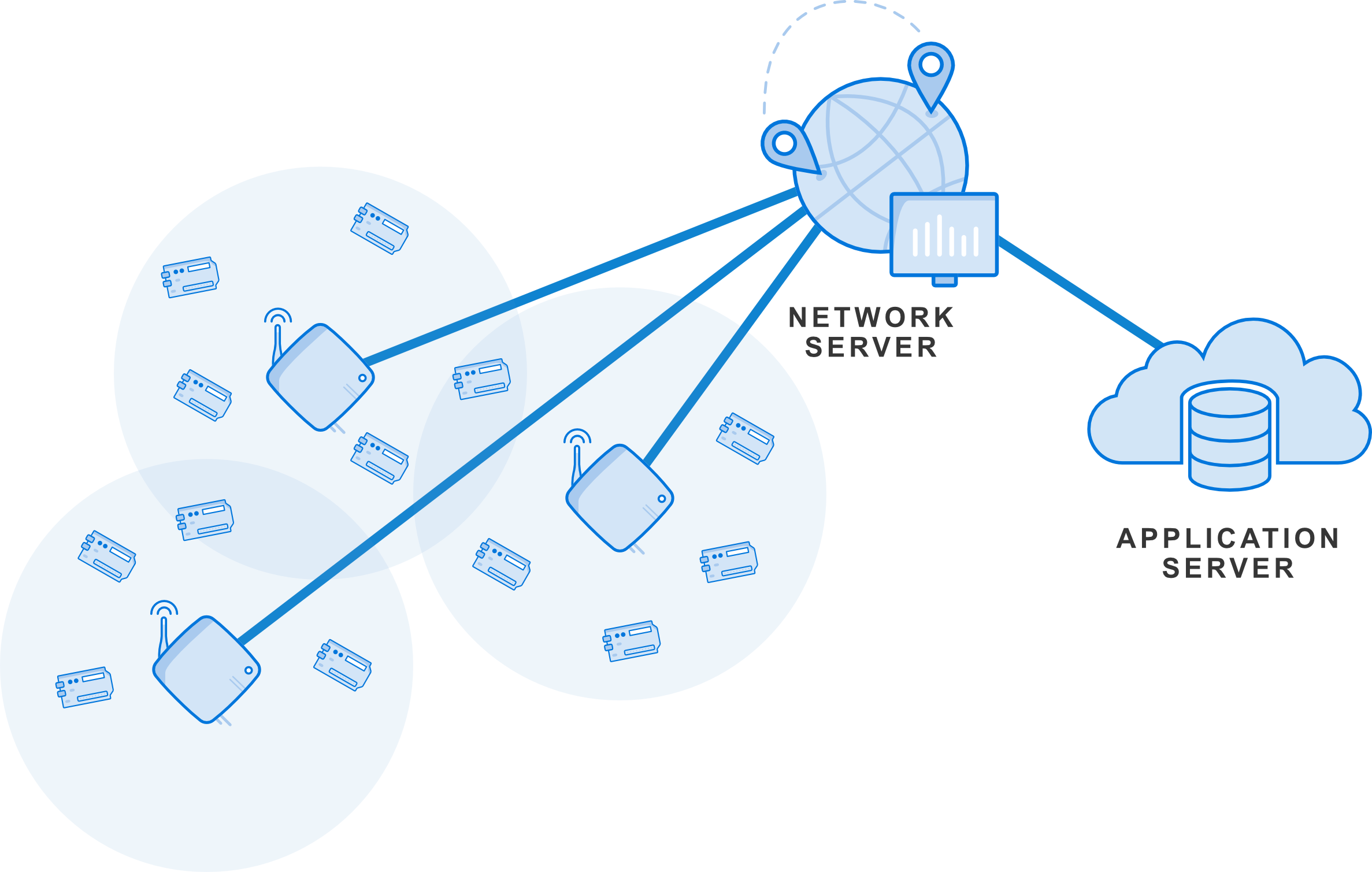
Uplink packets are received by the gateway(s), deduplicated (by the network server) and forwarded to the applications. Downlink packets are “broadcasted” by the gateways and received by the nodes. Operating LoRaWAN gateways is a community effort and does not require a license (e.g. The Things Network).
Packets sent by the nodes should be as small as possible. Depending on the data rate, the maximum payload size is between 51 and 222 bytes. Additionally, packets should only be sent every couple of minutes to save power and reduce flooding of the gateways.
Frequencies
LoRaWAN uses different frequencies depending on the region and regulations:
- 868 MHz in Europe
- 915 MHz in North America
- 433 MHz in Asia
- … (more depending on the frequency plans)
Security
LoRaWAN uses 128-bit keys for transport security. The Network Session Key (NwkSKey) admits a device to the network. The Application Session Key (AppSKey) is used to encrypt the payload.
Devices have to be activated before they can send data to the network. There are two ways to activate a device:
Over-the-Air Activation
When using OTAA, the devices sends a join request to a join server. This requires:
- The
DevEUI(address from IEEE EUI64 address space) which identifies the device (like a MAC address) and is supplied by the manufacturer. - The
JoinEUI(formerlyAppEUI) (address from IEEE EUI64 address space) which identifies the join server and is used to resolve the join servers IP address via DNS. - The
AppKey(128-bit AES key) which is used to encrypt the join request.
After sucessful activation a NwkSKey and AppSKey are generated and sent to the device to verify network communication and encrypt data.
Activation by Personalization
ABP uses static NwkSKey and AppSKey keys.
This approach is less flexible.