08 Architecture
Monolith
A monolith is an application that contains all its functionality in a single codebase and runs as a single process. Monoliths are easy to develop and deploy but can become difficult to maintain and scale as they grow in size and complexity.
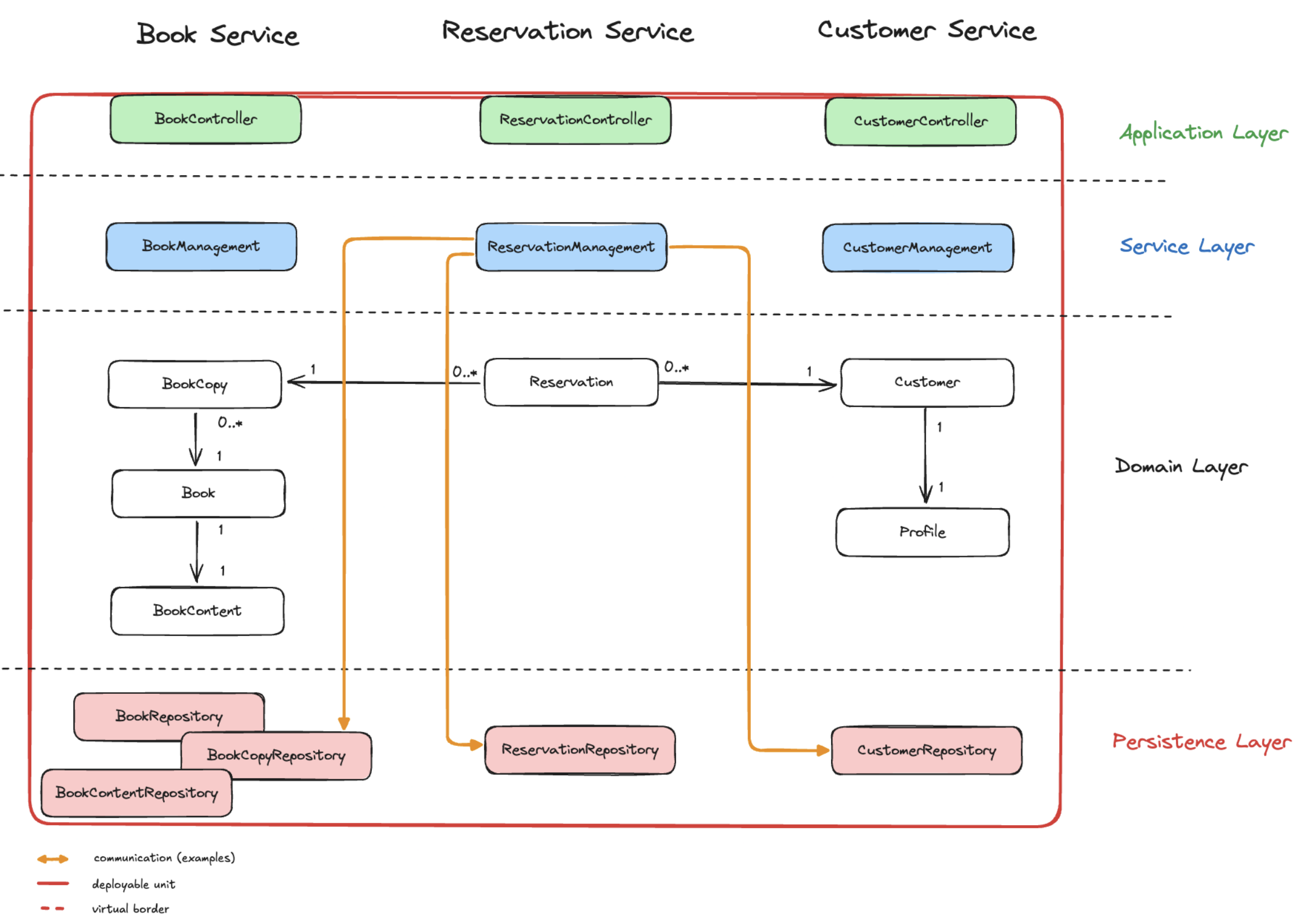
Microservices
Microservices are an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of small, independent services. Each service is responsible for a specific business function and communicates with other services over a network. Microservices are easier to maintain and scale than monoliths but require additional infrastructure and complexity.
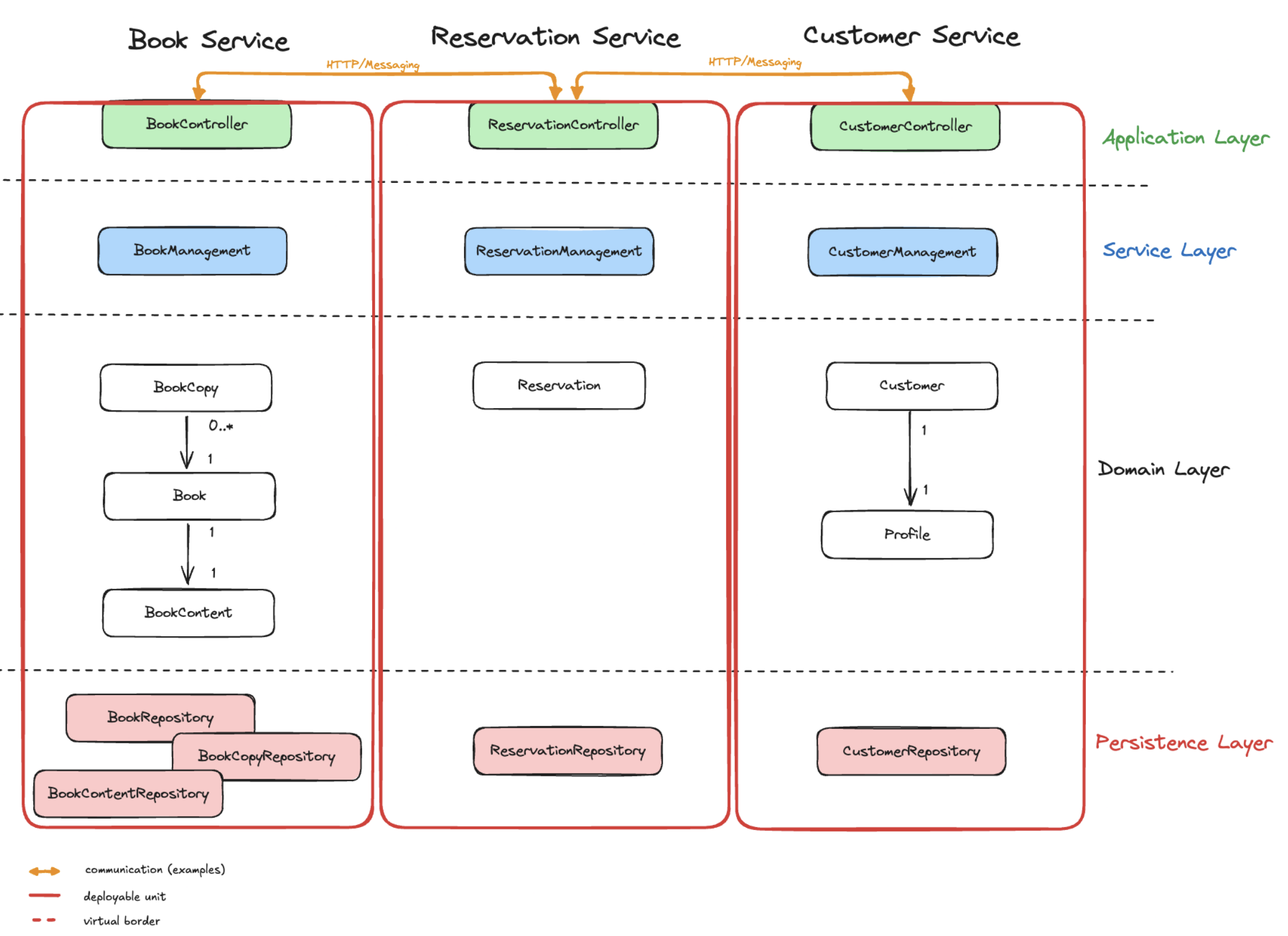
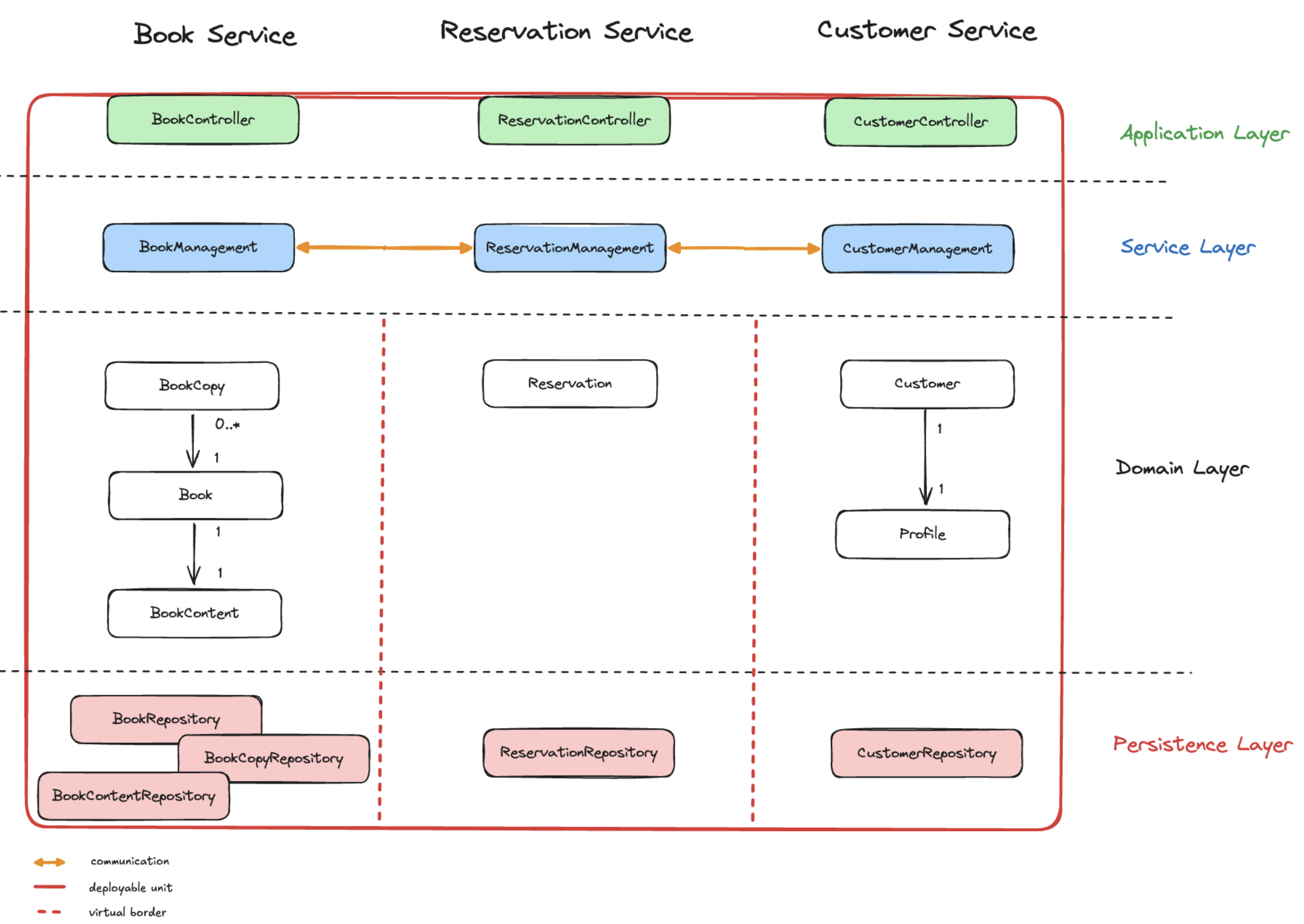
Modulith
A modulith is a hybrid architecture that tries to combine the benefits of a monolith and a microservices architecture. Moduliths are modular monoliths that are divided into modules that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. Moduliths are easier to maintain and scale than monoliths but do not have the complexity of a microservices architecture.
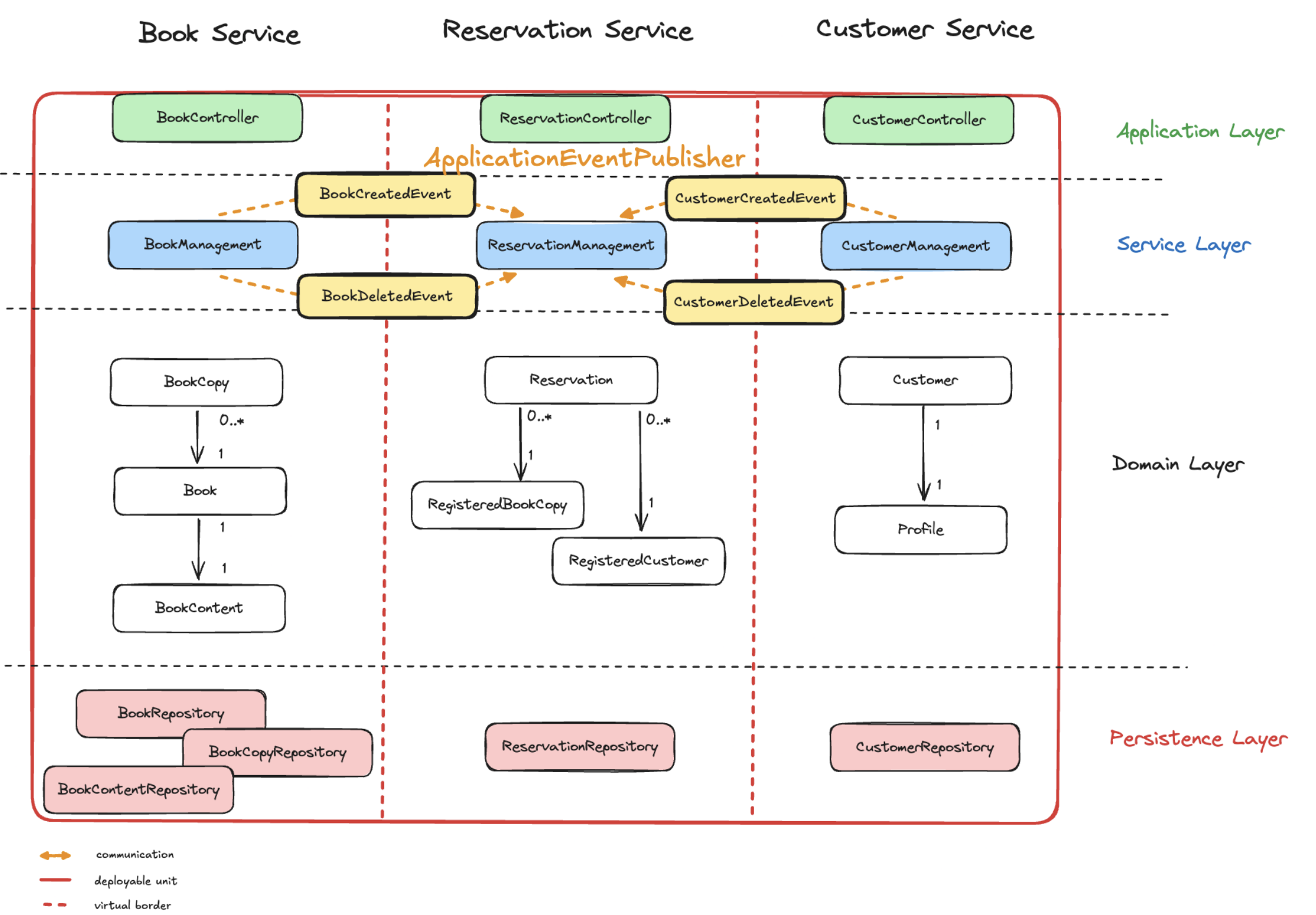
Event-Based Communication
Instead of creating dependencies between the different modules, moduliths use event-based communication to decouple the modules from each other. Modules can publish events to a message broker, and other modules can subscribe to these events to react to changes in the system. This allows modules to communicate with each other without creating direct dependencies between them.
Addendum: Spring Boot
This section contains content related to Spring Boot.
Request Flow
The Spring Boot request flow is a sequence of steps that occur when a request is made to a Spring Boot application. Most of the request pipeline is abstracted by Spring Boot, but it is important to understand the general flow of a request.
sequenceDiagram
box Blue Servlet Container
participant Client
participant Tomcat
end
box Green Spring Container
participant Filter
participant DispatcherServlet
participant HandlerMapping
participant Controller
participant Service
participant Repository
participant Database
end
Client->>Tomcat: GET /customers
Tomcat->>Filter: doFilter(..., chain)
Filter->>DispatcherServlet: doService()
DispatcherServlet->>HandlerMapping: getHandler()
HandlerMapping-->>DispatcherServlet: handler
DispatcherServlet->>Controller: handleRequest()
Controller->>Service: Request
Service->>Repository: Request
Repository->>Database: Request
Database-->>Repository: Response
Repository-->>Service: Response
Service-->>Controller: Response
Controller-->>DispatcherServlet: Response
DispatcherServlet-->>Filter: Response
Filter-->>Tomcat: Response
Tomcat-->>Client: HTTP 200 OK
Pros and Cons
| Monolith | Modulith | Microservices | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pros |
|
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
|
Addendum: Docker
This section contains content related to Docker.
Multi-Stage Builds
Multi-stage builds are a feature of Docker that allow you to use multiple build stages in a single Dockerfile. Each stage can have its own base image and build context, and the final image only contains the artifacts from the last stage.
# Build Stage
FROM eclipse-temurin:17 as build
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN ./gradlew bootJar
# Run Stage
FROM eclipse-temurin:17-jre
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=build /app/build/libs/library-*.jar library.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "library.jar"]
Networking
The docker bridge network is the default network for all containers in the same compose file. It is a private network that allows all containers to communicate with each other using their container name as the hostname. To expose a container port to the host machine, use port mappings.
Containers receive a dynamic IP address which changes every time the container is restarted. This is why it is recommended to use the container name as the hostname which are resolved by the internal DNS server.
Internet access from the docker bridge network is provided using a NAT gateway.